The brain is the control centre of the human body. It controls how we think, feel, communicate and move. Understanding how your brain works can help you understand stroke.
Brain cells
Specialized cells called neurons make the brain work. For neurons to work properly and survive, they need to be given a continuous supply of blood.
Blood vessels of the brain
Arteries and veins are types of blood vessels in your body. Arteries carry oxygen and nutrient rich blood to your organs. Veins carry waste away from your organs. Normal brain function needs a constant supply of oxygen and nutrients. The blood flow to the brain is disrupted when someone has a stroke. Therefore, some brain cells don’t get the oxygen and nutrients they require to live. When these cells die, that area of the brain cannot function the same as before.
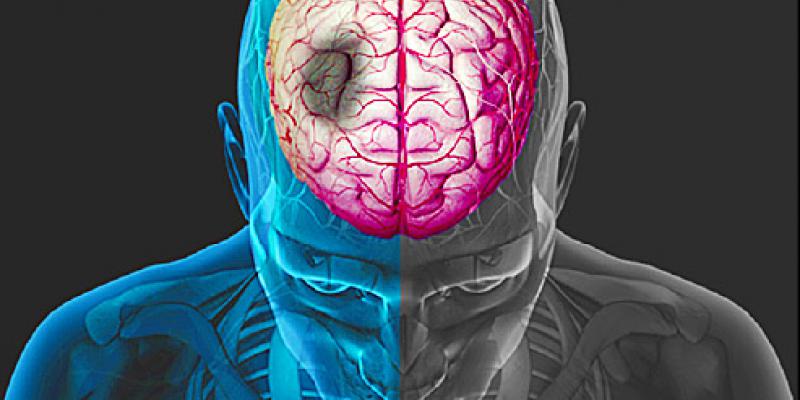
Hemispheres
The brain is divided into two parts called hemispheres, the right and the left. The right hemisphere controls the left side of your body. The left hemisphere controls the right side of your body. Some functions are controlled by both hemispheres.
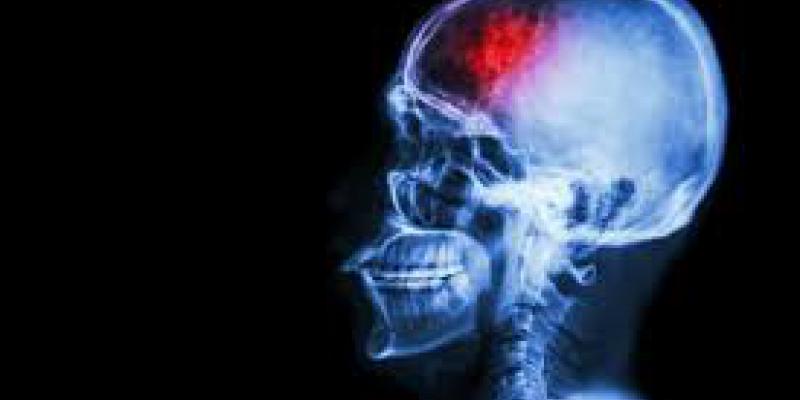
What happens during a stroke
A stroke happens when blood stops flowing to any part of your brain. This interruption causes damage to the brain cells.
Types of stroke
Ischemic stroke
Most strokes are caused by a blockage or clot in a blood vessel in your brain. This is called ischemic stroke. The blockage can be caused by a build-up of plaque on the inside wall of an artery. This grows as blood cells and fat cells stick to the plaque. Gradually, becoming large enough to block normal blood flow.
The blockage or clot can form either in an artery in your brain or in another part of your body and travel to your brain.
Transient ischemic attack (TIA)
A transient ischemic attack (TIA) is caused by a small clot that blocks an artery for a brief period of time. Sometimes TIAs are called a mini-stroke or a warning stroke. Symptoms from a TIA may only last a few minutes or hours. No lasting damage occurs. Nevertheless, TIAs are a medical emergency and you should call 9-1-1.
Hemorrhagic stroke
A hemorrhagic stroke is caused when an artery in the brain bursts, interrupting blood flow, which causes damage to the brain.
The major cause of hemorrhagic stroke is high blood pressure. This creates weak arteries over time, forming aneurysms and when they stretch too far, they will burst.
Other causes
In rare cases strokes can be caused by a tumour, infection, or brain swelling due to an injury/illness. Some people are born with irregularities in their arteries that can cause a stroke later in life.
How can a stroke affect my body?
The effects of stroke are different for each person. They can be mild, moderate or severe. The severity depends on factors such as:
- The type of stroke (ischemic or hemorrhagic)
- On which side of the brain the stroke happened (right or left hemisphere)
- Which lobes of the brain were affected
- The size of the damaged area in the brain
- The body functions controlled by the affected area
- The amount of time the brain area had no blood flow
- The time it took to get to hospital.
If you have any questions about stroke, don’t hesitate to ask one of our pharmacists at 519 Talbot Street.